Structure in C
struct add //abstract data type
{
int A,B;
}x,sum;
int main()
{
printf("Enter first no\n");
scanf("%d", &x.A);
printf("Enter second no \n");
scanf("%d", &x.B);
// adding nos
sum.A=x.A+x.B;
printf("Sum is = %d", sum.A);
return 0;
}
Passing structure to a function by references
#include <stdio.h>
struct sample
{
char OneArray[40];
float OneFloatVar;
};
void PassBy_Value(struct sample *s1);
int main()
{
struct sample sample1;
//printf("Enter some string \n");
//scanf("%s",&sample1.OneArray);
//printf("\nEnter float no \n");
//scanf("%f",&sample1.OneFloatVar);
passit(&sample1);
printf("\n %s ",sample1.OneArray);
printf("\n %f ",sample1.OneFloatVar);
return 0;
}
void passit(struct sample *s1)
{
strcpy(s1->OneArray,"Pass By Reference");
s1->OneFloatVar= 5.0;
}
Passing structure to a function by value
#include <stdio.h>
struct sample
{
char OneArray[25];
float OneFloatVar;
};
void passit(struct sample s1);
int main()
{
struct sample sample1;
printf("Enter some string \n");
scanf("%s",&sample1.OneArray);
printf("\nEnter float no \n");
scanf("%f",&sample1.OneFloatVar);
passit(sample1);
return 0;
}
void passit(struct sample s1)
{
printf("\n %s ",s1.OneArray);
printf("\n %f ",s1.OneFloatVar);
}
Command line argument in C
Environmental variable
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[], char * envp[]){
int i;
for (i = 0;
envp[i] != NULL; i++)
printf("\n%s", envp[i]);
getchar();
return 0;
}
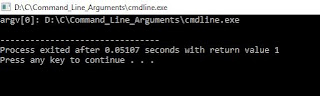
O/p:
#ifdev directives
#include <stdio.h>
#define YEARS_OLD 20
int main()
{
#ifdef YEARS_OLD 30
printf("Wikipedia is over %d years
old.\n", YEARS_OLD);
#endif
printf("Wikipedia is a great
resource.\n");
return 0;
}
O/p:
Multiline macros
#include<stdio.h>
#define PRINT(x, str) ({\
printf("The number %d", x);\
printf("
is ");\
printf(#str);\
printf("\n");\
})
int main() {
int x = 10;
if(x % 2 ==
0){
PRINT(x,
EVEN);
}
}
O/p:
Nested macros
#include<stdio.h>
#define Space(x) x*x
#define SpaceCost(x,y,z) (z*y + Space (x))
void main()
{
int
A=8,B=6,C=4;
printf("The Space of square= %d\n", Space(A));
printf("Cost of paint= %d\n", SpaceCost(A,B,C));
}
O/p:
Pragma
It is a compiler directive that allows one to provide extra
information to the compiler.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void func();
#pragma startup func
#pragma exit func
void main(){
printf("\nI am in main");
getch();
}
void func(){
printf("\n I am in func");
getch();
}
O/p:
Stringizing operator
#include <stdio.h>
#define mkstr(s) #s
int main(void)
{
printf(mkstr(This is Stringizing operator));
return 0;
}
O/p:
Token passing in C
#include<stdio.h>
#define paster(n) printf("\n value
=%d",tok##n);
main()
{
int
tok36=100;
paster(36);
//return
0;
}
O/p:
Qualifier
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
const int x =
10;
x = 12;
return 0;
}
O/p:
D:\C\QUALIFIERS\CONTST.c [Error] assignment of read-only variable 'x'











No comments:
Post a Comment